

VBOX_PATH_SHARED_LIBS = "/Applications/OpenSource/VirtualBox.app/Contents/MacOS" VBOX_PATH_APP_PRIVATE_ARCH = "/Applications/OpenSource/VirtualBox.app/Contents/MacOS" VBOX_PATH_APP_PRIVATE = "/Applications/OpenSource/VirtualBox.app/Contents/MacOS" If you like to change that, say into /Applications/OpenSource/VirtualBox.app/, you need to add the following to the LocalConfig.kmk:
#Virtualbox mac install
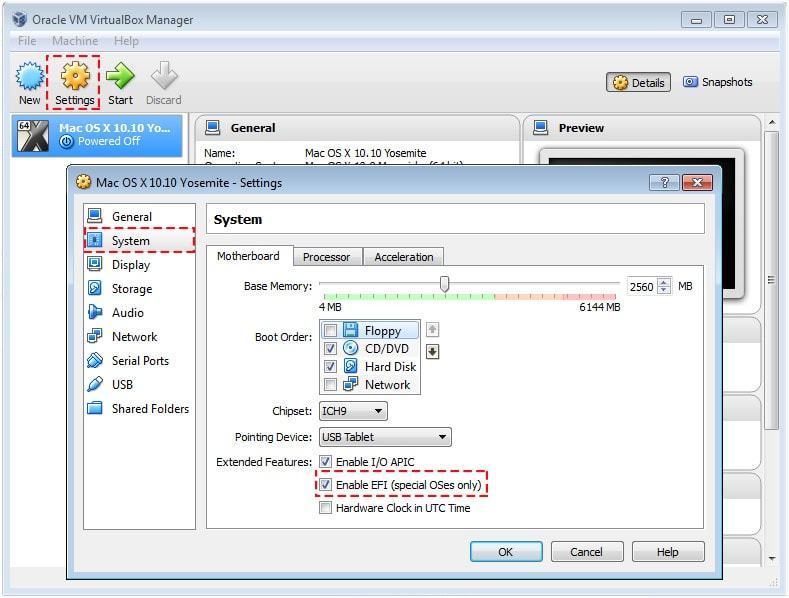
The default install directory of VirtualBox is /Applications/VirtualBox.app/. Hardening needs some additional configuration and post-build steps. Never disable hardening (see previous section) when creating packages for redistribution. Enter out/darwin.x86/release/dist/VirtualBox.app/Contents/MacOS/.Execute and make sure the modules loads successfully. These can be found in out/darwin.x86/release/dist along with a small script ( loadall.sh) to load them. Load all the kernel extension modules.The default is to a release build, should you wish to do a debug or profile build add BUILD_TYPE=debug or BUILD_TYPE=profile as argument to kmk or export it as an environment variable in your shell. Whenever you want to build VirtualBox, you have to open a shell and source the generated environment setup script env.sh, i.e.This step only has to be done once (if something changes in your build tool setup, you might have to repeat it but keep in mind that both output files will be overwritten). Also, it will create an environment setup script called env.sh. If it finds everything it needs, it will create a file called !AutoConfig.kmk containing paths to the various tools on your system. You can manually set the target architecture with -target-arch=x86 or amd64, if some architecture related problems occur. Change to the root directory of the sources and execute the configure script:.If you are running 10.10 (Yosemite) there is a boot-args option for allowing the loading of unsigned kexts. Loading self-built kernel extensions (kexts) on more recent OS X may require changes to the system config unless you have a kext signing certificate and is running 10.14 (High Sierra) or earlier.įor 10.11 (El Capitan) and later boot to the recovery partition and either enabling loading of unsigned kexts:įor 10.15 (Catalina) and later you also need to disable the reboot requirement (also from recovery partition):.Sudo port install libidl acpica yasm subversion doxygen texlive texlive-latex-extra texlive-fonts-extra x86_64-elf-gccĭoxygen, texlive* and x86_64-elf-gcc are optional (first two for documentation, latter for the validation kit). Until recently the official builds were done using Xcode 6.2 (you may use the tools/darwin.amd64/bin/ script to 'install' the necessary bits on later OS X versions).Īfter installing MacPorts, do not forget to make sure the following two lines are in your ~/.profile or ~/.zprofile file and actually loaded in the shell you're using:Įxport PATH=/opt/local/bin:/opt/local/sbin:$PATHĮxport MANPATH=/opt/local/share/man:$MANPATH
#Virtualbox mac mac os x
#Virtualbox mac windows
The program supports almost all versions of the most recent operating systems, such as Windows 10, Mac OS X Yosemite, and the latest updates of Ubuntu or any other Linux distribution. You have to take into account that these take part of the actual physical resources of your computer, so you need equipment that is powerful enough to run both the guest and host operating systems. The virtual disc where the system runs is completely customizable, and it lets you modify the virtual hardware to whatever specs you need, be it the processor, the RAM memory, or the storage capacity. VirtualBox is an open-source and multi-platform tool, available for Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X, as well as other operating systems, that lets you create virtual disc units where you can install a guest operating system, inside the one on your own computer, and use it as if it were actually installed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
